IS DECAFFEINATED COFFEE AS GOOD AS YOU EXPECT?
Decaffeinated Coffee, or Decaf Coffee, is ideal for those who still want to enjoy the taste of coffee without experiencing the stimulant effects of caffeine – like feeling jittery, heart palpitations, and insomnia. However, you still need to be aware of the appropriate dose and time to drink coffee to avoid affecting your health.
What is Decaf Coffee?
Decaf coffee, short for decaffeinated coffee, is coffee that has had its caffeine removed. Broadly understood, this is coffee from coffee beans that have had at least 97% of the caffeine removed before roasting and grinding. The nutritional value of this coffee will be close to that of regular coffee, the biggest difference is in the caffeine content.
The flavor of this coffee may become milder and the color may vary, depending on the producer’s method of processing the coffee.
History of Decaf Coffee
In 1820, Friedlieb F. Runge – a German chemist, succeeded in separating caffeine from coffee beans. From that foundation, in 1906, Ludwig Roselius – a businessman selling coffee – patented the first commercial process to create complete decaf coffee.
The method he used was to boil coffee with some specific acids, then use a benzene compound to decaffeinate. However, it has been disproved by medical standards because benzene is a potentially carcinogenic substance.
How much caffeine is in decaf coffee?
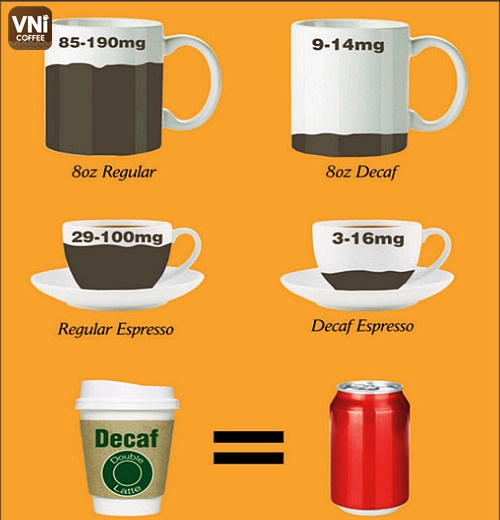
An average cup of regular coffee contains about 70 – 140mg of caffeine, depending on the type of coffee and method of preparation. Meanwhile, each 180ml of Decaf Coffee will only contain about 0-7mg of caffeine. As a result, you can avoid the harmful effects of consuming too much caffeine.
Its effects
- Reduce the risk of diabetes
A recent study by the American Diabetes Association (ADA) found that both regular and decaf coffee contain ignans and chlorogenic acid that are effective in glucose metabolism while reducing oxidation. in the body. In addition, the magnesium component also reduces the risk of diabetes. Every cup of coffee you drink daily can reduce your risk by up to 7%.
- Prevent neurodegenerative diseases
Studies on human cells show that Decaf Coffee can protect nerve cells in the brain, thereby helping to prevent the development of many neurodegenerative diseases, including Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s. This may be because the chlorogenic acid in coffee helps reduce the risk of dementia and neurodegenerative diseases.
- Limit digestive diseases
In some cases when drinking coffee, you may experience unwanted side effects such as heartburn or acid reflux. You can solve this problem with Decaf Coffee because it has been shown to cause less acid reflux than regular coffee. In addition, if you drink 2 cups of decaf coffee a day can also reduce the risk of developing colon cancer by 48%.
- Enhance liver function
The cafestol found in coffee has the function of protecting the body against certain substances that are harmful to the liver, such as aflatoxin. It is this substance that stimulates the production of glutathione, an antioxidant that enhances liver function and detoxifies the body.
Accordingly, scientists from the National Cancer Institute, Maryland (USA) conducted a study on 27,793 participants aged 20 and older. The volunteers were given 3 cups of coffee (both decaf and regular coffee) a day between 1999 and 2010. The results showed that the people who drank 3 cups of pure coffee per day. have lower liver enzyme levels than those who don’t drink coffee.
How to make decaf coffee
All current decaf coffee production processes are carried out by separating the caffeine from the beans when they are freshly harvested and separated from the fruit, unroasted and pre-processed, but ensuring that all ingredients are retained. other compounds.

Here are three common ways to remove caffeine from the beans:
- Specialized solvents
Compounds such as Ethyl and Methylene chloride will be used to decaffeinate according to a natural chemical reaction. The US Food & Drug Administration (FDA) has recognized these two substances as safe for human health.
- Swiss Water method:
This method relies on the soluble and osmotic properties of caffeine to remove them from the coffee beans, without using any chemical by-products. Initially, the coffee beans are soaked in hot water so that the caffeine breaks down inside this solution. However, not only caffeine but also sugar and other factors that make up the unique coffee taste are also separated.
After the above step, solution 1 (containing water, caffeine, sugar, and coffee flavoring agent) is poured through a filter made of charcoal. Due to the chemical nature of charcoal, the caffeine molecules will be trapped in the filter, while other ingredients pass through easily. From there, we have solution 2 containing only water, sugar, and coffee flavoring. This part of solution 2 continues to be used to reset, returning to the heating step and soaking a new batch of raw coffee beans. At this point, because the solution medium is saturated with sugar and coffee flavor from batch 1, only the caffeine of batch 2 is separated. Therefore, the second batch of beans will keep the original coffee flavor.
- CO2 liquid
Raw coffee beans will be put in a sealed steel barrel, completely separate from the outside environment. Then, CO2 liquid is added to start the process. The chemistry of liquid CO2 allows it to bind only to caffeine, not to other ingredients.
The pressure in the chamber will be adjusted to 1000 pounds/square inch to increase the decaffeination efficiency. After the successful separation of caffeine, the chamber space will be pressurized again. The liquid CO2 becomes a gas and automatically evaporates from the coffee beans.






